They are found in all of the southern U.S., mostly in the western deserts.
They are common in woodpiles, on rocky hillsides, in garden sheds and outhouses.
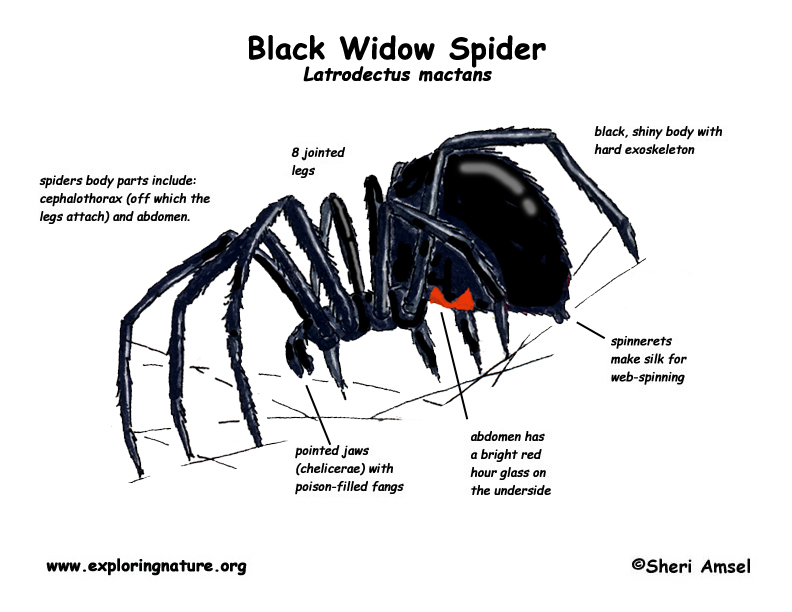
They are not large spiders. Their body is about 1.5 inches long. Females are shiny black with a red hourglass- shaped mark on their round belly (abdomen). Males are half the female’s size with longer legs and light streaks on its belly (abdomen).
The black widow is not a bold (aggressive) spider. The female hangs belly up in her web and rarely leaves it, but she will bite if bothered. Only the female has a poisonous bite. The venom is 15 times as toxic as that of a rattlesnake.
They eat flies, moths, crickets, small reptiles and other small animals. Their fangs shoot venom into prey to kill it and digestive juices to make its body soft for easier eating.
The female eats the male after mating. Then lays 25 – 900 eggs in an oval, brown, papery egg sac. They hatch after about 3 weeks.
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Arthropoda
Class: Arachnida
Order: Araneae
Family: Theridiidae
Genus: Latrodectus
Species: L. mactans
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Spider (Black Widow)" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 13, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/Spider-Black-Widow >