Ears, cochlea, semicircular canals
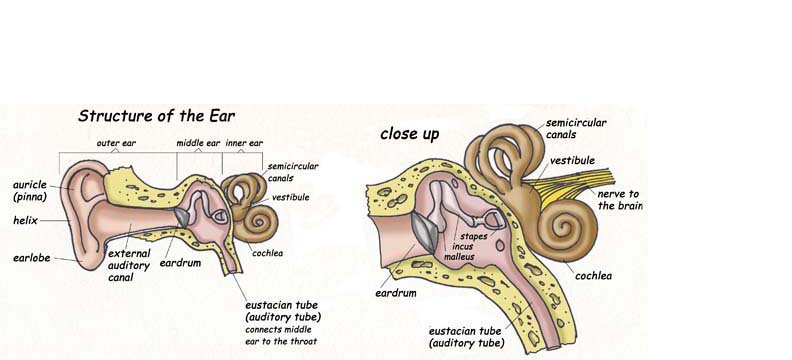
The ear has 3 areas: the outer, middle and inner ear. The outer ear is the ear that you see on the side of your head. It is called the auricle or pinna and its job is to focus sound into the ear. The sound passes through a canal called the external auditory canal that ends at the eardrum. Sound waves hit the eardrum (or tympanic membrane) and make it move (vibrate).
The middle ear (or tympanic cavity) is where you find the 3 smallest bones of the body; the malleus (hammer), incus (anvil) and stapes (stirrup). They send the sound vibrations from the eardrum through the oval window into the inner ear. The middle ear also has an opening into a tube that runs down into the throat ( the eustacian tube or auditory tube). Swallowing or yawning opens that tube and equalizes the air pressure in the middle ear. This is called ear popping.
The inner ear is filled with fluid, which collects the vibrations coming from the middle ear and brings them to the hearing receptors. The inner ear is made up of 2 parts; the bony labyrinth and the membranous labyrinth. The bony labyrinth is cave-like structure, made of bone where the 3 parts of the inner ear sit. The membranous labyrinth is made up of the 3 organs inside the bony labyrinth. The vestibule and the semicircular canals are involved with keeping your balance and equilibrium and knowing the position of your head (which is important). The cochlea is a spiral shaped chamber (looks like a snail) that houses the "cochlear duct" which has the hearing receptors; the "organ of corti."
To protect your hearing you should never put anything into your ear. Even a cotton swab meant for cleaning earwax should not be put inside your ear canal because it can puncture your eardrum. You also can destroy hearing receptors by listening to really loud music for a long time. Over time it can make you deaf.