They are found in the tropical and subtropical waters of the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans.
When they are small hatchlings, they hide in floating seaweed and ocean debris (styrofoam, tar balls, and plastic bits). As they get larger, they move to coral reef.
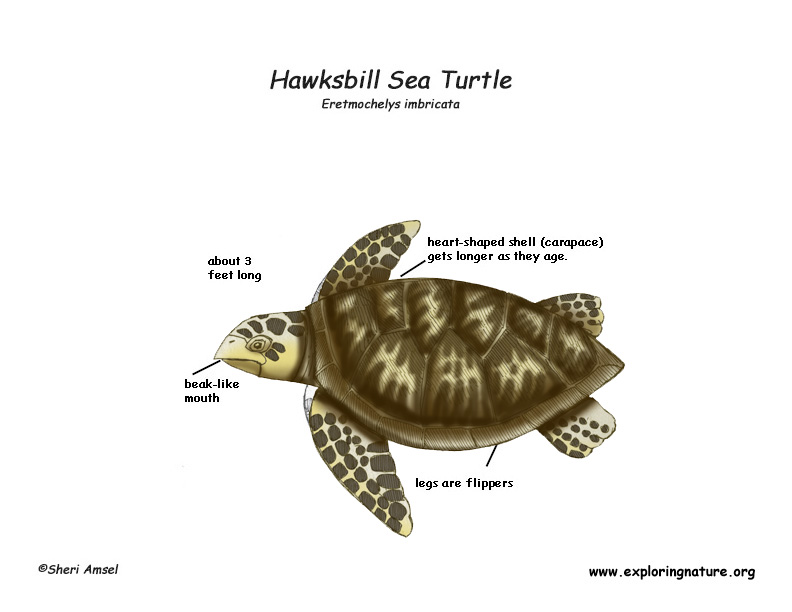
They have a beak-like mouth. They have 2 claws on each flipper. Their shell (carapace) is heart-shaped in young turtles and becomes longer as they age. Their head is long and comes to a point at their pointed mouth. Nesting females weigh about 175 pounds. This is a medium–sized sea turtle.
They use the caves and ledges in coral reefs as places to rest.
They eat sponges found on coral reefs.
Ocean pollution and man are their only real threat.
Females come out of the ocean onto the beaches in the Caribbean at night from July to October. They dig a pit in the beach, lay about 140 eggs, and fill in the nest. It takes 1 – 3 hours. Females will nest about 4 times in one season, every 2 weeks. Eggs hatch in 2 months.
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Class: Reptilia
Order: Testudines
Suborder: None
Family: Cheloniidae
Genus: Eretmochelys
Species: E. imbricata
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Sea Turtle (Hawksbill)" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 15, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/513 >