American elk are found in the Rocky Mountains and Pacific Northwest of the United States and Canada.
Elk are found in many habitats, from deep forests and rocky slopes to alpine meadows and mountain ridges.
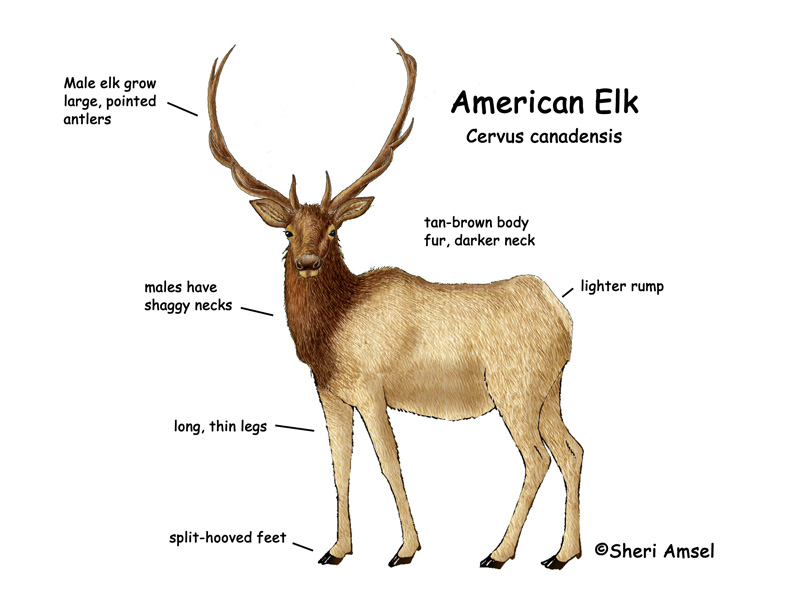
They have a grayish coat with a lighter colored rear end. Males can weigh up to 1000 pounds, while the females only reach 600 pounds. Male elk grow large antlers that can weigh 30 pounds. They lose them in early spring after mating season.
During mating season, in the fall, male elk “bugle.” Their bugle is a shrill call to round up their “harem” of females. They travel in herds of up to 25 elk.
Elk eat grass, twigs and bark.
Predators are mountain lions, wolves, coyotes, grizzly bears and man.
Each female has 1 young in late May to early June. They are pregnant for 8.5 months (gestation).
They live up to 15 years in the wild. They are listed as Lower Risk - Least Concern.
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Artiodactyla
Family: Cervidae
Subfamily: Cervinae
Genus: Cervus
Species: Cervus elaphus
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Elk (American)" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 13, 2024
< http://exploringnature.org/db/view/332 >