Physical Science For Grade 1
Next Generation of Science Standards (NGSS) - Grade 1
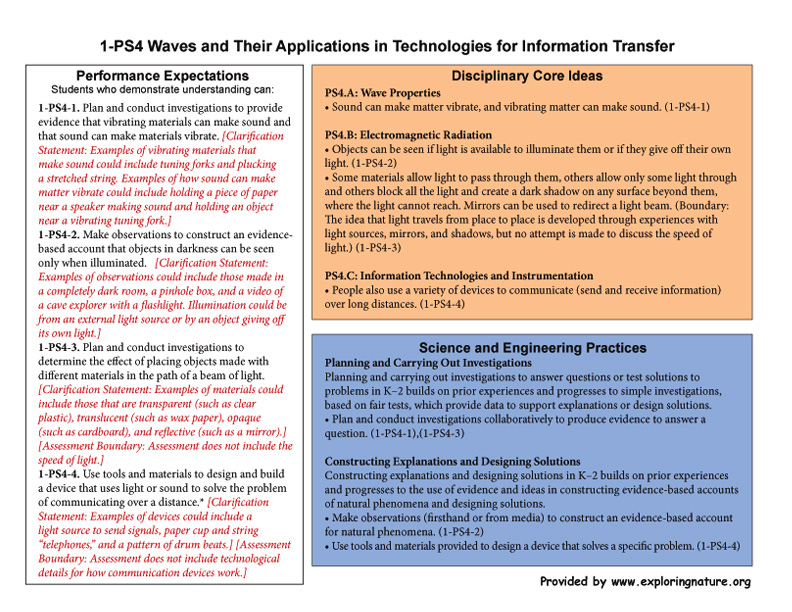
Disciplinary Core Ideas
PS4.A: Wave Properties
• Sound can make matter vibrate, and vibrating matter can make sound. (1-PS4-1)
PS4.B: Electromagnetic Radiation
• Objects can be seen if light is available to illuminate them or if they give off their own light. (1-PS4-2)
• Some materials allow light to pass through them, others allow only some light through and others block all the light and create a dark shadow on any surface beyond them, where the light cannot reach. Mirrors can be used to redirect a light beam. (Boundary: The idea that light travels from place to place is developed through experiences with light sources, mirrors, and shadows, but no attempt is made to discuss the speed of light.) (1-PS4-3)
PS4.C: Information Technologies and Instrumentation
• People also use a variety of devices to communicate (send and receive information) over long distances. (1-PS4-4)
Science and Engineering Practices
Planning and Carrying Out Investigations
Planning and carrying out investigations to answer questions or test solutions to problems in K–2 builds on prior experiences and progresses to simple investigations, based on fair tests, which provide data to support explanations or design solutions.
• Plan and conduct investigations collaboratively to produce evidence to answer a question. (1-PS4-1),(1-PS4-3)
Constructing Explanations and Designing Solutions
Constructing explanations and designing solutions in K–2 builds on prior experiences and progresses to the use of evidence and ideas in constructing evidence-based accounts of natural phenomena and designing solutions.
• Make observations (firsthand or from media) to construct an evidence-based account for natural phenomena. (1-PS4-2)
• Use tools and materials provided to design a device that solves a specific problem. (1-PS4-4)
Crosscutting Concepts
Cause and Effect
• Simple tests can be designed to gather evidence to support or refute student ideas about causes. (1-PS4-1),(1-PS4-2),(1-PS4-3)
Connections to Nature of Science
Influence of Engineering, Technology, and Science, on Society and the Natural World
• People depend on various technologies in their lives; human life would be very different without technology. (1-PS4-4)
Performance Expectations
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
1-PS4-1. Plan and conduct investigations to provide evidence that vibrating materials can make sound and that sound can make materials vibrate. [Clarification Statement: Examples of vibrating materials that make sound could include tuning forks and plucking a stretched string. Examples of how sound can make matter vibrate could include holding a piece of paper near a speaker making sound and holding an object near a vibrating tuning fork.]
1-PS4-2. Make observations to construct an evidence-based account that objects in darkness can be seen only when illuminated. [Clarification Statement: Examples of observations could include those made in a completely dark room, a pinhole box, and a video of a cave explorer with a flashlight. Illumination could be from an external light source or by an object giving off its own light.]
1-PS4-3. Plan and conduct investigations to determine the effect of placing objects made with different materials in the path of a beam of light. [larification Statement: Examples of materials could include those that are transparent (such as clear plastic), translucent (such as wax paper), opaque (such as cardboard), and reflective (such as a mirror).] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include the speed of light.]
1-PS4-4. Use tools and materials to design and build a device that uses light or sound to solve the problem of communicating over a distance.* [Clarification Statement: Examples of devices could include a light source to send signals, paper cup and string “telephones,” and a pattern of drum beats.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include technological details for how communication devices work.]
Common Core State Standards Connections
ELA/Literacy
W.1.2 Write informative/explanatory texts in which they name a topic, supply some facts about the topic, and provide some sense of closure. (1-PS4-2)
W.1.7 Participate in shared research and writing projects (e.g., explore a number of “how-to” books on a given topic and use them to write a sequence of instructions). (1-PS4-1),(1-PS4-2),(1-PS4-3),(1-PS4-4)
W.1.8 With guidance and support from adults, recall information from experiences or gather information from provided sources to answer a question. (1-PS4-1),(1-PS4-2),(1-PS4-3)
SL.1.1 Participate in collaborative conversations with diverse partners about grade 1 topics and texts with peers and adults in small and larger groups. (1-PS4-1),(1-PS4-2),(1-PS4-3)
Mathematics
MP.5 Use appropriate tools strategically. (1-PS4-4)
1.MD.A.1 Order three objects by length; compare the lengths of two objects indirectly by using a third object. (1-PS4-4)
1.MD.A.2 Express the length of an object as a whole number of length units, by layering multiple copies of a shorter object (the length unit) end to end; understand that the length measurement of an object is the number of same-size length units that span it with no gaps or overlaps. Limit to contexts where the object being measured is spanned by a whole number of length units with no gaps or overlaps. (1-PS4-4)
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Grade 1 - 1-PS4 Waves and Their Applications in Technologies for Information Transfer" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. April 17, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/1952 >